What is it?
The NETSCOUT Arbor Edge Defense (AED) solution is cyber protection at the network edge. NETSCOUT AED is uniquely positioned on the network edge (between the internet router and the firewall) to provide an inline, always-on, first and last line of defense. Using stateless packet processing, continuous global threat intelligence, decades of DDoS protection and mitigation expertise and patented adaptive DDoS defense technology, AED can automatically stop inbound/outbound and dynamically changing cyber-attacks.

Why should you care?
Organizations are under constant risk from all types of advanced cyber threats. And as many of those organizations undergo digital transformations, cyber criminals uncover opportunities to capitalize on these efforts. Non-stop and ever-evolving DDoS attacks, ransomware, phishing attempts, and data breaches have forced these organizations to continually invest, evaluate and improve their defenses. Protecting and controlling the network edge is the most critical first step in defending an organization from these continuous cyber-attacks.
How does it work?
Deployed in between the firewall and internet router, and using highly scalable stateless packet processing technology, Arbor Edge Defense acts as a network edge threat intelligence enforcement point where it blocks in bulk, inbound cyber threats (e.g. DDoS attacks, IOCs) and outbound malicious communication — essentially acting as the first and last line of cyber threat defense for an organization at the network perimeter. With Adaptive DDoS and Cyber Anomaly Protection, AED utilizes automated traffic analysis algorithms based in AI and ML to detect attacks, identify the nature of the attack and recommend specific countermeasures or configuration changes to optimally block that attack.
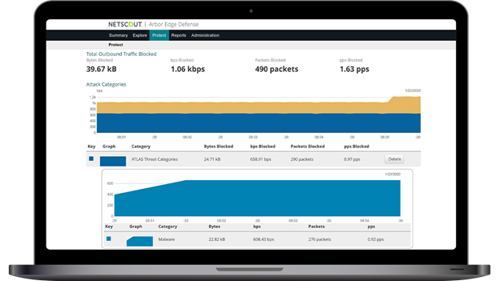
NETSCOUT monitors in real-time over 425 Tbps of internet traffic across over 500 ISPs, over 1200 enterprise sites and in 93 countries. This represents between 40-50% of the global internet traffic at any given time. This data is collected in NETSCOUT’s ATLAS cloud infrastructure where NETSCOUT continuously runs AI/ML algorithms that generate an analysis pipeline, so NETSCOUT can continuously update the adaptive technology and anomaly detection being utilized by AI/ML engine implemented in the AED. These updates can be provided in real time through our ATLAS subscription feeds or made available to customers from the NETSCOUT support center.
Differentiation in the market
The NETSCOUT AED utilizes the world’s most sophisticated adaptive technology. The integration of AI and ML combined with the data analysis performed in NETSCOUT’s ATLAS cloud infrastructure allows our edge solutions to provide deterministic, predictable results without requiring manual human review. This adaptive automated approach to cyber detection and mitigation has proven to be far more effective than developing and deploying rule-sets created through human intervention.
One of the significant value-add uses cases for the Arbor Edge Defense solution is in a passive detection mode for cybersecurity assessments. AED can detect all types of cyberattacks and traffic anomalies that may be contributing data breaches, ransomware, or malware deployments. Often these types of network events go unchecked and undetected with normal firewall and IDS deployments.
How to position and sell Arbor Edge Defense
Along with adding significant adaptive cyber defense capabilities to the edge of the customer’s network and digital footprint, the Arbor Edge Defense solution significantly reduces the burden on the downstream network infrastructure, making firewalls, routers and load balancers more efficient and effective while extending their capacity and ultimately increasing the value of their investment.
Introduce AED to customers who are:
- Deploying new firewalls
- Thinking about upgrading their existing firewalls due to capacity issues
- Having unexplainable application performance issues that are often caused by undetected low and slow DDoS attacks
- Been hit with recent data breaches or business-disrupting cyber attacks
Learn more
About the author


