Working Principle of SMPS Power Supply
Like other types of power supply, a SMPS power supply transfers power from a source — usually an AC outlet — to a DC device. What sets the SMPS apart is its ability to regulate the output voltage. It can increase or decrease the output voltage to maintain a constant output regardless of changes in load. This dual ability gives it an advantage over linear regulators, which can only regulate the output down (that is, they can only decrease the voltage, not increase it).
SMPS Operation Diagram
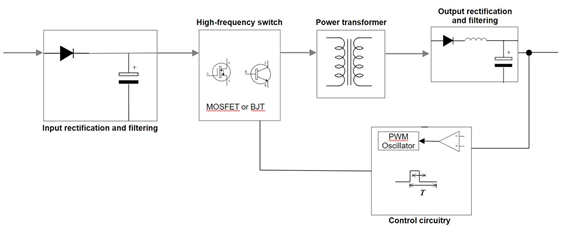
The diagram above outlines how the SMPS operates. An SMPS’s functionality is more complex than that of a linear regulator, but we can break it down into five stages:
1. In the first stage, the incoming AC power runs through a rectifier and undergoes filtration to produce DC
2. The SMPS works at high frequencies, so a high-frequency switch processes the DC signal, which creates a high-frequency pulsating DC signal
3. The power transformer steps down the high-voltage DC signal to a DC signal of the appropriate level
4. The stepped-down DC signal is rectified and filtered to a achieve a steady, constant DV output
5. The control circuitry monitors the output voltage and adjusts the high-frequency switch on-the-fly to ensure a continuous output stream of the desired voltage

