Microcontrollers are everywhere, whether you’re driving your car, on your computer reading this (or smartphone/tablet) or making a cup of coffee on your coffee machine. With IoT rapidly increasing and data constantly being gathered, microcontrollers are a huge part of the modern world.
What is a Microcontroller?
A microcontroller (sometimes called an MCU or Microcontroller Unit) is a single Integrated Circuit (IC) that is typically used for a specific application and designed to implement certain tasks. Products and devices that must be automatically controlled in certain situations, like appliances, power tools, automobile engine control systems, and computers are great examples, but microcontrollers reach much further than just these applications.
Essentially, a microcontroller gathers input, processes this information, and outputs a certain action based on the information gathered. Microcontrollers usually operate at lower speeds, around the 1MHz to 200 MHz range, and need to be designed to consume less power because they are embedded inside other devices that can have greater power consumptions in other areas.
Inside a Microcontroller: Essential Components
A microcontroller can be seen as a small computer, and this is because of the essential components inside of it; the Central Processing Unit (CPU), the Random-Access Memory (RAM), the Flash Memory, the Serial Bus Interface, the Input/Output Ports (I/O Ports), and in many cases, the Electrical Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (EEPROM). Figure 1 shows a great diagram of the main parts and also other parts in the microcontroller. Let’s dive into each of these components and see how they work inside the microcontroller.
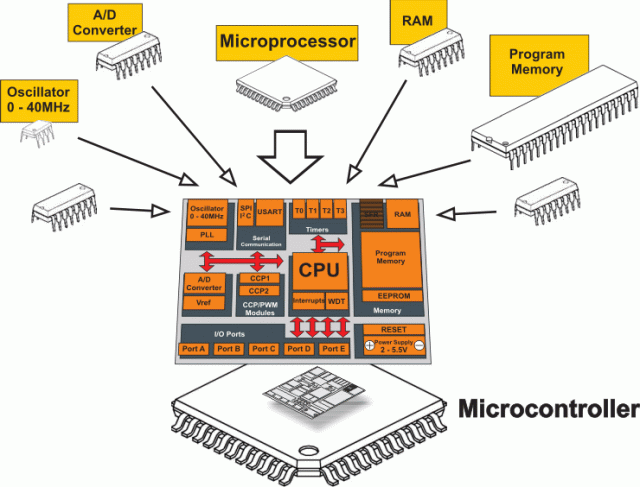
Figure 1: Parts of a microcontroller. (Source: Max Embedded)
Design of Microcontroller CPU
The CPU, sometimes called a processor or microprocessor, controls all of the instructions/data flow that it receives. You can think of it as the brains of the system, processing all the data input it receives and executes the required instructions. Its two main components are the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), which performs arithmetic and logical operations, and the Control Unit (CU), which handles all of the processor’s instruction executions. Figure 2 shows a usual "machine cycle" that the CPU goes through.
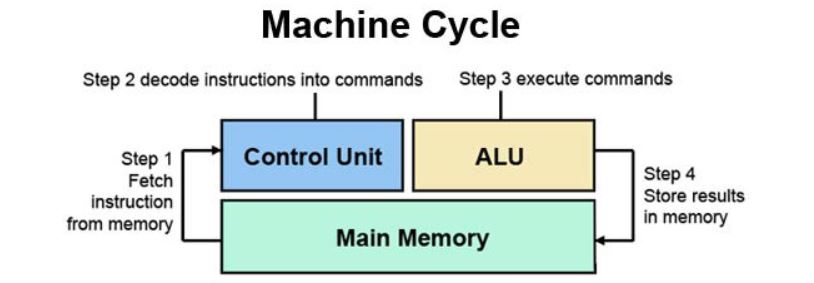
Figure 2: A typical machine cycle that the CPU executes. (Source: Computer Hope)
Microcontroller RAM
RAM is a component that temporarily stores data, and can be accessed quickly. It provides quick read-and-write access to the storage device. This differs from most other memories as it takes longer for data to be extracted since the data isn’t readily available. You can see it as RAM having access to the surface of data – easily reachable – but anything that dives deeper will require a different type of memory. RAM improves total system performance because it allows the microcontroller to work with more information at the same time. Since RAM is temporary data, its content is always erased when the microcontroller is shut down.
Use of Flash Memory in Microcontrollers
Flash Memory is a type of non-volatile memory that, unlike RAM, retains its data for an extended period, even if the microcontroller is turned off. This keeps the saved program that you might have uploaded to the microcontroller. Flash Memory writes to a “block” or “sector” at a time, so if you need to just re-write one byte, Flash Memory will need to re-write the whole block that the byte is in, which can wear out quicker.
What is EEPROM in Microcontrollers?
EEPROM is like Flash Memory, being a non-volatile memory and retaining its data even after shutdown. The difference is that, while Flash Memory re-writes a “block” of bytes, EEPROM can re-write any specific byte at any time. This extends the life of EEPROM compared to Flash Memory, but also means that it is more expensive.
Serial Bus Interface
A Serial Bus Interface is the serial communication in the microcontroller, sending data one bit at a time. With microcontroller boards, it connects ICs with signal traces on a printed circuit board (PCB). For ICs, they use serial bus to transfer data to reduce the number of pins in a package making them more cost effective. Examples of serial buses in ICs are SPIs or I2Cs.
Microcontroller I/O Ports
I/O ports are what the microcontroller uses to connect to real-world applications. Inputs receive changes in the real-world, from temperature sensing, to motion sensing, to push buttons, and much more. The input then goes to the CPU and decides what to do with that information. When it’s time to do a certain command based on a certain value from the input, it sends a signal to the output ports, where it can range from a simple LED light going off, to running a motor for a certain part, to many more. Figure 3 shows some common input and output components.

Figure 3: Common inputs and output components that are used for microcontroller. (Source: Marshall Ball)
관련 상품 참조
관련 상품 참조
Hopefully this gives you a better idea what a microcontroller is, as well as some insight into the most important parts of a microcontroller. If you want to learn more about popular electronic components, you can check some of these articles out:
Know the Difference Between an Inverter, Converter, Transformer and Rectifier.
Read the different major types of Motion Sensors and how their physics make them work.
Look at the difference between the popular microcontroller, the Arduino Uno Rev3, and the popular SBC, the Raspberry Pi 3.





