The recognition that climate change is a real threat to the sustainable continuation of our lifestyle, has driven an explosion in alternatives to fossil fuel-based transportation. From the early 2000s, the emergence of electric-gas hybrid and fully electric vehicles (EV) has accelerated dramatically.
Advances in battery technologies and machine learning have created new excitement for electric vehicles and most traditional car manufacturers have electric vehicle lines coming to market. In addition to sustainability objectives, higher emissions standards, falling EV technology prices, increases in battery energy densities and more widespread charging infrastructure are all making EV vehicles the future of transportation.
The need for electric vehicle charging and safety standards
With traditional and new entrants using a variety of technology approaches towards electric vehicles, it is critical that standards are established to ensure that EV technologies are reliable. Malfunctions in the electronics in the automobile and the charging infrastructure could have fatal consequences for occupants and other persons involved along with rescue teams. Safe operation and reliability of batteries, controls, plug connectors, switches, and wires need to be assured for peace of mind and accident avoidance. Regulatory frameworks that establish benchmarks for various EV component technologies and offer a certification process for providers will increase consumer confidence, safety, and supplier compliance. The key benefits of establishing global standards and certifications include:
- Safety of personnel, product, and charging infrastructure
- Interoperability so a common infrastructure can be utilized
- Cost reduction to ensure mass production and accessibility of EV technology
- Increased adoption of new technologies underpinning the EV revolution
Several standards are published at the global level by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and transposed in supra-national and national versions. The ensuing sections of this article delineate the standards and the areas where these standards are most applicable.
Overview of the main international electric vehicle safety and charging standards
Currently, there is no single global EV standard. Many of the major EV production centers – including Japan, Europe, North America, and China – are promoting differing ideas in a variety of areas. Although regulatory certifications usually follow technological innovation they serve as an important rite of passage to access the EV marketplace. By stipulating basic guidelines for safety and environmental compliance, regulatory standards impact the evolution of the technology. For EV vehicular technologies, four main areas constitute the bulk of the regulatory and standard setting efforts:
- Safety and security
- Charging connectors
- Charging topology
- EV charging related communications
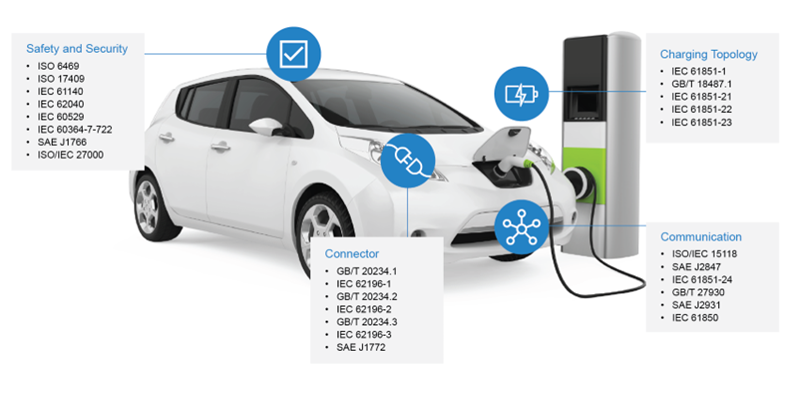
Figure 1: Overview of key EV standards
Electric vehicle safety and security standards
EVs require rigorous safety testing. The same safety standards required for conventional vehicles also apply to EVs. The safety standard covers a wide range of specific details pertaining to information management, privacy, installation, occupant injury prevention, and insulation against electric shock. The safety issues of EVs are largely covered by the international standard ISO 6469. This standard has three parts:
- On-board electrical energy storage, i.e., the battery
- Functional safety means protection against failures
- Protection of persons against electrical hazards
The table below describes the safety and security standards outside of ISO 6469.
| Standard Name | Description |
| ISO/IEC 27000 | Provides best practice recommendations on information security management including privacy, confidentiality, and IT/technical/cybersecurity issues |
| IEC 60364-7-722 | Low-voltage electrical installations - Part 7-722: Requirements for special installations or locations - Supplies for electric vehicles |
| SAE J1766 | Ensures adequate barriers between occupants and battery systems to protect from potentially harmful factors and materials within the battery system that can injure occupants of the vehicle during a crash |
| ISO 17409 | Safety requirements for conductive connection of EVs to external electric circuits |
| IEC 61140 | Protection against electric shock. Common aspects for installation and equipment |
| IEC 62040 | Uninterruptible power systems (UPS) |
| IEC 60529 | Degrees of protection provided by enclosures (IP Code) |
Electric vehicle charging connectors
The EV charging connector or plug type standard varies across geographies and models. While there is no consensus on an universal plug technology, there is a critical mass of global automakers supporting the Combined Charging System (CCS) in North America and Europe. Japanese automakers use CHArge de MOve (CHAdeMO), and China – the world’s largest electric vehicle market uses GB/T. All the standards intend to define a common electric vehicle conductive charging system architecture including operational requirements and the functional and dimensional requirements for the vehicle inlet and mating connector.
In North America, SAE J1772 (IEC 62196 Type 1), also known as a J plug, is the standard for electrical connectors for electric vehicles. Maintained by the SAE International and formally titled "SAE Surface Vehicle Recommended Practice J1772, SAE Electric Vehicle Conductive Charge Coupler", it covers the general physical, electrical, communication protocol, and performance requirements for the electric vehicle conductive charge system and coupler.
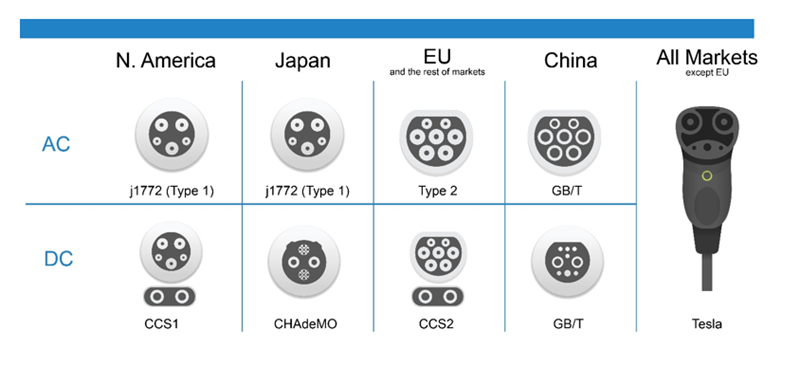
Figure 2: EV Connector Types
Charging station and EV communication
Today, very few charging stations (both at home and public) are smart grid-enabled, and even fewer cars allow for V2G (vehicle to grid) connectivity. However, rising EV penetration is likely to increase the need for common standards for charging infrastructure and interoperability between charging stations, distribution networks, and the EVs themselves. Interoperability is key not only to shield from charging infrastructure vendor lock-in but also to allow for cost-effective connectivity of EVs with diverse charging infrastructure and metering.
ISO15118 – an international standard for bi-directional digital communications between electric vehicles and the charging station – defines a V2G communication interface for bi-directional charging/discharging of electric vehicles. ISO15118 is a key enabler of the “plug & charge” capability, allowing EV drivers to insert the charger plug into the car, charge, and drive away when ready. This process is enabled by a digital certificate in the vehicle, allowing it to communicate with the charging point management system (CPMS). This enables a seamless end-to-end charging process, which includes automatic authentication and billing, and avoids the need to use an RFID card, an app, or to memorize PINs.
Here is the list of common standards on EV communication:
| Standard Name | Description |
| ISO/IEC 15118 | Communication interface for bi-directional charging/discharging of electric vehicle |
| SAE J2847 | Communication between plug-in vehicles and off-board DC chargers |
| IEC 61851-24 | Electric vehicle conductive charging system - Part 24: Digital communication between a DC EV charging station and an electric vehicle for control of DC charging |
| SAE J2931 | Security requirements for digital communication between the Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE) and the utility, ESI, Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI), and/or Home Area Network (HAN) |
| IEC 61850 | Communication networks and systems for power utility automation - ALL PARTS |
Electric vehicle charging standards
The IEC 61851 standard pertains to electric vehicle conductive charging systems. The standard describes four charging modes. The first three modes deliver AC current to the EV on-board charger; however, mode 4 delivers DC current directly to the battery and bypasses the on-board charger. Mode 3 employs several control and protection functions with the goal of public safety.
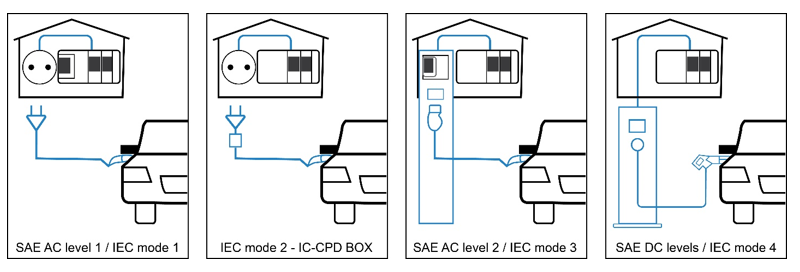
Figure 3: EV Charging Topologies
| EV Charging | Description |
| Mode 1 | Charging with AC on a typical household wall outlet, either 1 or 3 phase, with currents up to 16A. In this mode, there is no communication between the energy source/grid and the vehicle. Ground fault interrupter (GFI)/residual current detector (RCD) should be installed on the infrastructure side |
| Mode 2 | Like mode 1, with higher currents and a control and protection equipment integrated into the in-cable control and protection device (IC-CPD). The IC-CPD protects from electrical hazards in case of isolation failures |
| Mode 3 | Charging with AC takes place through a dedicated charging outlet connected to a stationary charger (or wallbox). Charging is controlled via communication between the charging unit and the vehicle |
| Mode 4 | Charging with DC is useful when charging with a high amount of power. In IEC mode 4 there is a dedicated wallbox with a fixed charging cable and a dedicated DC charging plug |
Future of electric vehicle standards and regulations
Electric vehicle proliferation will be widespread as the world grapples with climate change and environmental sustainability. Cost reduction, technological advances, and multiple suppliers are all driving dramatic innovations in EV technology. Global electric vehicle standards can further speed up the adoption of EV technology and increase the safety compliance of EVs. Just as with traditional automobiles, safety and reliability are the key thrusts of the various standards in use across the globe. Vehicle and charging infrastructure safety and security, connectors, charging topology, and EV communications are the main areas covered by today's standards. Despite the prevalence of different standards, there is a critical mass in various geographies to drive a harmonious adoption of EV standards across the globe.
References
Innovation Outlook: Smart Charging for Electric Vehicles



