Wasilios Pitharas, Application Engineer at Samsung Electro-Mechanics (SEMCO), explores how the construction of an additional copper epoxy layer, commonly known as soft termination, protects the vital inner ceramic material of an MLCC.
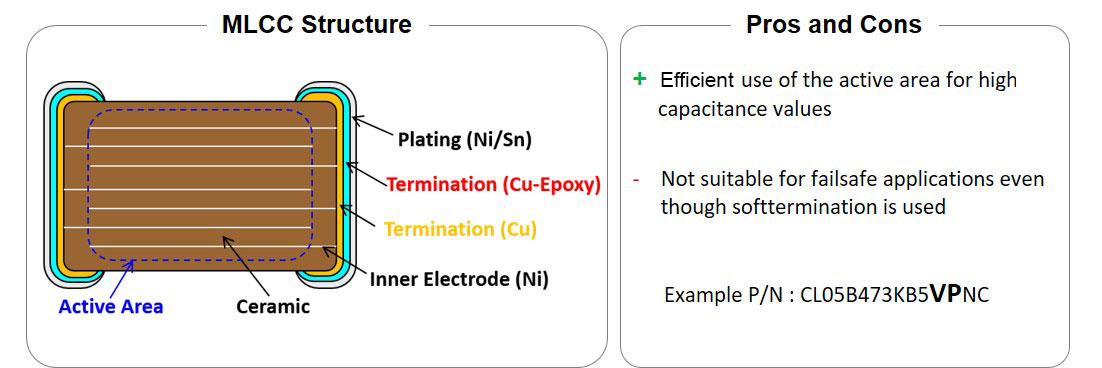
Construction of a standard class II automotive MLCC
Ceramic layers are usually printed with a nickel paste (electrode) and then stacked on top of each other. The capacitance is determined by the ceramic material, the electrode’s arrangement and the number of layers. Subsequently, a copper layer is added to the termination, which connects the electrodes and ensures good conductivity. Compared to other manufacturers, SEMCO MLCCs add an additional copper epoxy layer, commonly known as soft termination. This extra layer acts as a buffer for mechanical stress and protects the more sensitive ceramic against breaking. Finally, a nickel-tin plating is added as last outer layer to avoid oxidation and to ensure solderability.
Minimize security risk
Why is the additional protection in the form of a soft termination needed and what happens if the ceramic cracks?
As the insulation resistance between the soft termination layers decreases, the ceramic material creates an insulator as a cavity. But, a short circuit between two opposing layers can occur. Depending on the applied voltage, this can lead to an immense thermal power loss, which can destroy the component and make the entire circuit board inoperative. For this reason, automotive manufacturers create their own quality standards.
For example, VW Group defined the VW80808 standard, which includes the "MLCC failsafe strategy". This strategy aims to minimize the mentioned security risk by setting a guideline of which products can be used in which applications.
If a short-circuit causes a power loss of >2.5W, or if it significantly impairs a system’s function [1], the failsafe strategy must be used. This is particularly the case when battery voltage (terminal 15, 30) is applied directly to the component.
VW’s standard offers four options to keep the failsafe strategy. Out of these, all SEMCO product types use a soft termination layer and are qualified according to AEC-Q200. Option number one can be used in every electric system. The other options are limited to the 12V electric system.
I. Series connection of two mutually orthogonal capacitors
The first option that can be used independently of the electric system voltage is the orthogonal placement of two capacitors in series. Image 2 shows this setup in a simplified circuit diagram.

If one of the two capacitors is placed unfavorably to bending stress, the orthogonal arrangement ensures that a backup capacitor remains intact. Since both capacitors are connected in series, the isolation to ground potential is still given.
II. Series capacitor
A Series or "Flexisafe" capacitor uses the previously demonstrated principle of a series connection of two capacitors in a single component. The opposing layers of different potential are not directly above each other. A “floating” layer connects them.
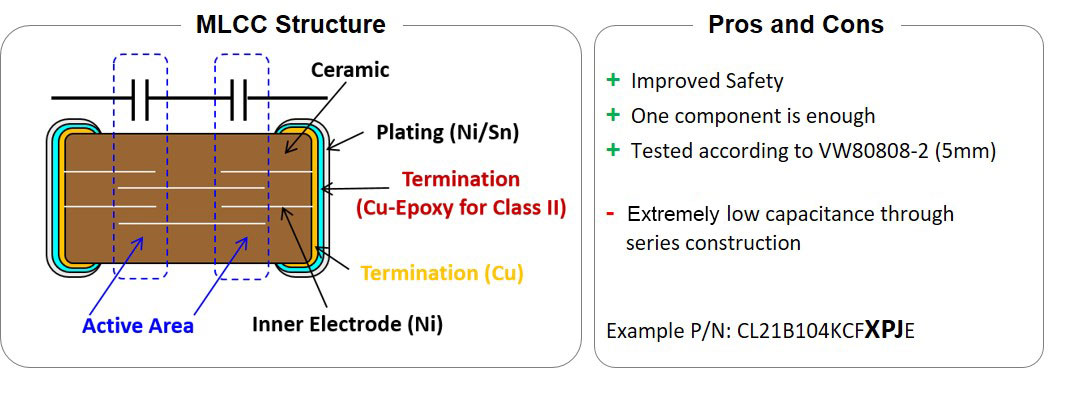
However, the internal structure extremely limits the capacitance value. Compared to the previous solution, the principle of series connection plays a role as well as the reduction of active area.
III. Open Mode Capacitor
If a crack would occur in the red marked "risky" area, it is less likely to end in a short circuit as only layers of the same potential would touch each other due to the shorter electrodes.

IV. Capacitor with Soft Termination
The advantages of using a capacitor with soft termination include a higher mechanical resistance and an ideal utilization of the available component dimensions. If the layer structure is identical to a standard component, there is no performance gap.
All SEMCO Automotive Class II capacitors have a soft termination. So, why are standard components without soft termination unsuitable in failsafe applications? The reason is that the use of a component with soft termination is only permitted in VW Group, and if it has been tested according to VW 80808-2 (Appendix A "Qualification of MLCC with soft termination"). This standard requires performing several thermal and mechanical stress tests in a row. The most critical tests are the 5mm bending (“Board Flex”) and the moisture resistance test.
Standard automotive components from SEMCO are also tested according to VW80808-2, but with a bending limit of 3mm. This is above the market standard of 2mm for comparable components. The use for the automotive sector is guaranteed, but not for fail-safe applications. When you talk about soft termination in the market, you usually associate it with 5mm bending strength and the failsafe strategy. Here a differentiated approach must be done for SEMCO. The separate product family “PJ” covers the required 5mm bending strength. The qualification according to VW 80808-2 was performed here with regular criteria.
For low and medium capacitance values, additional layers of the same potential are placed on the top and bottom inside the component’s body. In the case that an MLCC would crack, the risk of a short circuit is reduced extremely, which results in an increased mechanical stability of the complete MLCC.
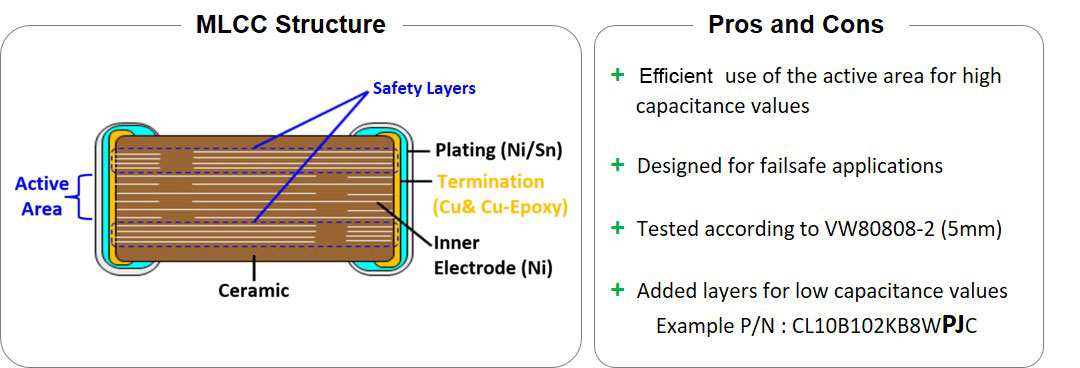
The soft-termination tests according to VW 80808-2 were successfully completed for all actively promoted SEMCO Automotive components.
Downsizing
The trend of miniaturization (downsizing) supports the use of the soft termination option even more. The key to small and safe components is both a robust termination and a fine ceramic powder, which enables a thinner layer structure.
Product inquiries
If you would like to learn more about any of the products mentioned in this article, please reach out to Mr. Mokhtar Marzouk at Mokhtar.marzouk@samsung.com.
Sources:
[1] VW 80808-1: 2015-02, Page 9
[2] VW 80808-2, Appendix A „Qualifikation von MLCC mit Softterminierung“
Image 1: Standard SEMCO Class II Automotive MLCC Samsung Electro-Mechanics (SEMCO)
Image 2: Orthogonal Setup of two Standard Automotive Capacitors Samsung Electro-Mechanics (SEMCO)
Image 3: Series Capacitor Samsung Electro-Mechanics (SEMCO)
Image 4: Open Mode Capacitor Samsung Electro-Mechanics (SEMCO)
Image 5: PJ Series - 5mm Bending Samsung Electro-Mechanics (SEMCO)


