Preventative Maintenance uses historical data to anticipate when a part is likely to fail so that it can be replaced beforehand but expensive parts can be replaced when they still have useful life in them. And parts can fail prematurely so unscheduled downtime can still occur. For Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning and Refrigeration (HVACR) systems in buildings, this means staff in offices are inconvenienced or can’t work. This can be even worse for buildings such as hospitals where HVACR is mission critical to proper operations.
Preventive Maintenance enables the ability to see how each critical component is performing in real time and can accurately predict when it needs to be replaced. This new Predictive Maintenance approach creates the ‘smarts’ with the full coverage of sensors for condition monitoring and an ecosystem to process the data.
RelatedContent
Webinar (above): How to Enable Predictive Maintenance and Condition Monitoring for HVACR Devices
Tech Article: How Predictive Maintenance can cut costs and increase reliability by putting the ‘smarts’ into smart buildings
Predictive Maintenance – a Definition
Traditionally, maintenance has been about checking that machinery appears to be running correctly, cleaning it and replacing a part when it fails. This could happen at any time and production has to stop while it is fixed. This unscheduled downtime can be very disruptive and costly.
The solution, called Preventative Maintenance, is to work out the average life of each component, which is known as the Mean Time Before Failure (MTBF). This enables a schedule of replacement of parts to be created so that they are replaced before the MTBF is reached. Now, downtime occurs when it has the least impact based on when failures are anticipated to occur.
However, it is only a partial solution as parts can fail earlier than expected so expensive unscheduled downtimes can still occur. There is also a downside to this approach in that parts could be replaced when they are still perfectly functional with plenty of operational life in them, which is an unnecessary cost.
These two issues can be solved by actually knowing when a failure is going to happen so that remedial action can be taken beforehand. This is known as Predictive Maintenance. The predictions come from having real time data from sensors on the performance of key components. This is combined with the intelligence to recognize when something is starting to go wrong so that it can be fixed at a convenient downtime. Thus, parts are only replaced when they need to be, solving the second issue.
An Analogy Between Weather Forecasting and Maintenance Schemes
• Traditional Maintenance is going for a walk today. If it rains, you buy an umbrella and put it up.
• Preventative Maintenance is looking at historical records to see if it typically rains on this day of the year. If it usually does, you buy an umbrella for today, but it might not actually rain.
• Predictive Maintenance is gathering data from various locations over time so that an accurate prediction on whether it will rain or not can be made. You only buy an umbrella if rain is predicted.
Challenges and Preconditions
To continue the weather analogy, the accuracy of weather forecasting has improved over the years because more data points are available. In addition, the computer algorithms are more sophisticated making predictions better and better. And so, it is with Predictive Maintenance, the more data points that can be gathered, the better able is the system to be aware of what is happening and thus give more accurate predictions.
In practical terms, this means sensors positioned on critical components to gather the data on their real time status and performance – known as Condition Monitoring. These sensor-equipped parts are also known as Internet of Things (IoT)- enabled devices. IoT has been forecasted to be huge but, until now, has not grown at the rate expected. This is because it needs sensors that deliver the performance required in small packages at the right price point so that they can be prolifically used. Infineon has solved this bottleneck with its XENSIV™ range of best-in-class sensors that set new standards for performance and low power within small and robust packages. It provides an extensive range to address all the commonly required types of sensors needed, providing the foundations upon which to build Predictive Maintenance and Condition Monitoring solutions.
The Range of XENSIV™ Sensors
• Gas sensors for CO₂ to monitor indoor air quality - XENSIV™ PAS CO₂
• Barometric air pressure sensors for air flow measurement - XENSIV™ DPS368
• MEMS microphone for noise anomaly detection XENSIV™ IM69D130
• 24 GHz Radar and 3D Magnetic Sensors for detection of mispositioned motors and compressors - XENSIV™ BGT24LTR11 and XENSIV™ TLI493D-A2B6
• Current sensor for motors and compressors - XENSIV™ TLI4971
• Hall effect magnetic sensor for vibration monitoring - XENSIV™ TLE4997E2
To complement the sensor range, Infineon offers microcontrollers for data processing with optional integrated Wi-Fi or Bluetooth connectivity, and the OPTIGA™ Trust M security controller IC for highly secure, cloud access by devices.
Also, an increasing number of products have performance monitoring built in such as Infineon’s intelligent digital power supplies and motor control solutions in its iMotion class of products. These generate data that can be used for Predictive Maintenance.
Gathering the Data
The second challenge is being able to handle and process the huge amount of data in real time to identify the start of any deviations from normal parameters. The larger the incoming dataset and the more sophisticated the analysis algorithms, the more reliable and accurate becomes the Predictive Maintenance and therefore the greater the cost savings it provides.
This huge volume of data management requires edge processing, i.e. funneling data from various sensors into a microcontroller where it can be processed from raw data into intelligent information. This is then sent on for further processing to make decisions about the status of components. Infineon provides microcontrollers such as the XMC4700 that are designed specifically for this task along with security to protect the data from the edge to the cloud. Called OPTIGA™ Trust M, this hardware-based security IC provides authentication and with multi-account registration.
Ecosystem Overview
To help further Predictive Maintenance solutions, Infineon has teamed up with Amazon Web Services (AWS), a part of Amazon, to provide the cloud services to handle and analyze the data harvested. It has also partnered with Klika Tech, an IoT service provider who supports customers to integrate intelligence and cloud services to their products.
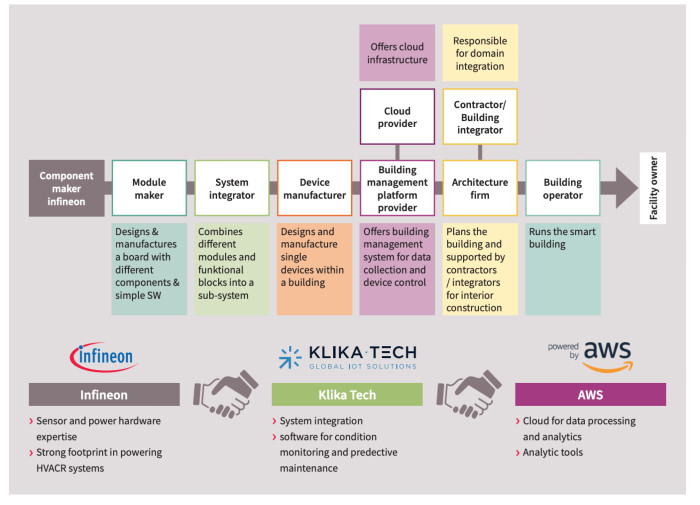
Figure 1: The value chain for smart building technology – a complex ecosystem
The Evaluation Kit
This provides a simple-to-use starting point for customers to see how easy it is to use the integrated solution from the three companies to create their own products for the markets they want to address. Customers can focus on their value add of creating the specific solutions for their target markets, safe in the knowledge that critical areas, which form the foundations of the value chain for Predictive Maintenance solutions, have already been addressed and solved.
The kit has an adapter board that provides a reference setup so that a variety of different configurations to be evaluated and includes barometric air pressure and temperature, magnetic current and Hall or MEMS microphone sensors with others available as required.
The board has an Infineon XMC4700 microcontroller that runs the FreeRTOS software framework and the OPTIGA™ Trust M high-end hardware security solution. In addition, a basic set of software is included that handles the collection of data, pre-processing it and then sending it to the AWS cloud for full processing. The kit thus provides a platform for testing solutions for real-time, edge-to-cloud data management.
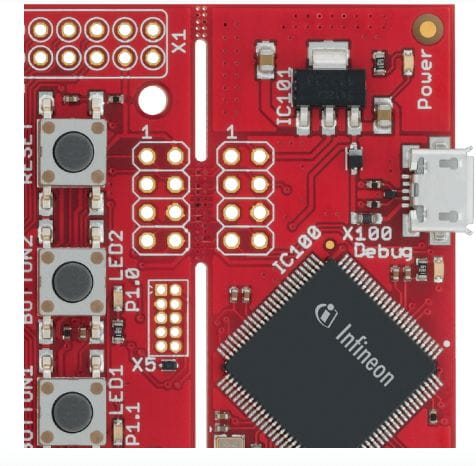
Figure 2: Infineon Evaluation Kit
Predictive Maintenance in HVACR – a Working Demonstration Unit
Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning and Refrigeration (HVACR) is an excellent example of a suitable area for Predictive Maintenance inside a building as equipment failure can cause severe problems and costs. To demonstrate how such a system works, Infineon, Klika Tech and AWS have created demonstrator units using portable air conditioning units. Condition monitoring checks the status of critical components such as compressors, motors, fans in real time so that any anomalies can be immediately detected, and Predictive Maintenance performed. In this case (Figure 3), the current flow of the cold fan, the hot fan and the compressor are monitored and processed to provide an easy-to-read dashboard that alerts to any anomalies along with air-flow monitoring using barometric pressure sensors.
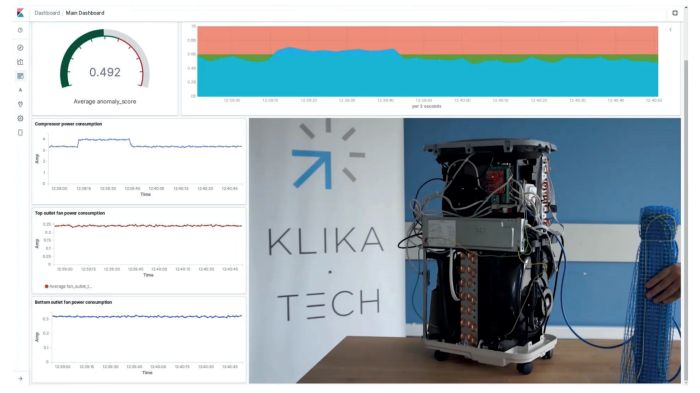
Figure 3: HVAC demonstration unit (on the right) and the real-time sensor data for condition monitoring (on the left)
Example of Dirty Air Filter
An Infineon barometric air pressure sensor monitors the air flow rate in an HVACR system. The graph shows it to be slowly declining because the air filter is becoming clogged and it will need to be cleaned or replaced before it reaches the point where it places a strain on the motors. This is a much more accurate and reliable system than simply changing or cleaning the filters at regular intervals. It detects the amount of actual dirt build up, which can be very variable on a day-to-day basis, and can be used to adjust the maintenance scheme to only when actually needed and thus save costs.
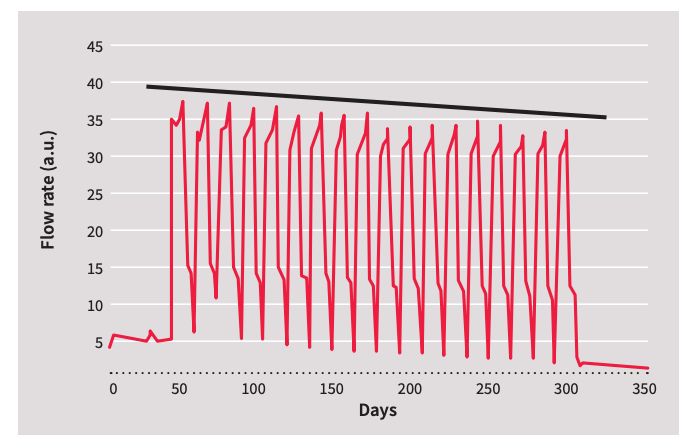
Figure 4: The decrease of the air flow rate in HVACR over time due to clogging filter
Key Benefits
- Predictive Maintenance is a data-enabled maintenance scheme that takes an equipment’s real-time condition into account by sensor-empowered monitoring
- Predictive Maintenance helps to detect and fix failures of devices inside a building at an early stage and use advanced analytics to predict them before they happen
- Predictive Maintenance reduces downtime and maintenance costs
- Predictive Maintenance increase’s transparency on building operations
- Predictive Maintenance improves offered value-add services (e.g. Maintenance)
General Applications
• Smart Buildings
See More from Infineon
Explore Infineon’s Smart Building
Discover What’s New from Infineon
Ver Productos relacionados
Ver Productos relacionados
Ver Productos relacionados
Ver Productos relacionados
Ver Productos relacionados
Ver Productos relacionados
Ver Productos relacionados
Ver Productos relacionados





