NTC thermistors can be used to sense temperature, while RFID tags can be used to control medical products and have quite convenient applications in medical products. This article will introduce NTC thermistors and RFID products introduced by Murata, and analyze their product characteristics for your reference in the development of related products.
NTC thermistors are common temperature sensors
NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) thermistor is a kind of device whose resistance will decrease with the increase of temperature and can be used in temperature sensing and other applications. It is a sintered non-oxide ceramic made of manganese (Mn), nickel (Ni), cobalt (Co), and other elements. Electrodes can be formed in the ceramic. Lead type and chip type are common thermistors in appearance and shape. The resistance value of NTC thermistors varies with temperature, ranging from 1% to 5%/℃. It is a common temperature sensor in many electronic devices.
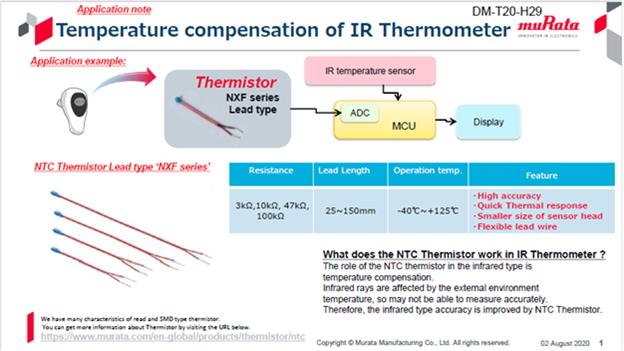
The NTC thermistor made by Murata adopts devices with high precision and good thermal response. The diversified product range includes not only various shapes (SMD chip and lead types), but also covers a variety of applications, such as temperature detection, overheat detection, circuit protection, current control, heating, and other applications. In particular, the NXF series belongs to a flexible lead type and is quite suitable for temperature sensing.
As NTC thermistors are extremely sensitive to temperature changes and the change value of resistors is quite stable, they are quite suitable for application in electronic thermometers. Murata's NXF series of lead-type NTC thermistors are compact in size and fast in response, with flexible lead lengths ranging from 25 to 150 mm. The excellent ceramic technology made by Murata enables these NTC thermistors to meet various requirements of customers for characteristics. The NXF series of NTC thermistors support a wide range of specifications.
RFID tags assist in managing medical devices
In the process of surgery, all kinds of surgical tools must be used, and the management of these tools has also become a problem for many medical staff. Because of this, U.S. regulations require that a UDI (Unique Device Identifier) must be placed on each surgical tool by 2020 to regulate that medical institutions should apply UDI to all medical devices for safe use and storage. Subsequently, Europe has promulgated similar regulations and plans to complete them by 2027.
The requirement of placing a UDI on each surgical tool has become a worldwide trend. However, due to the variety and shape of medical instruments, it is really difficult to use manual recording and accurately manage the use time. In addition, it takes quite a lot of time and manpower to assemble and inspect the toolset. Even for skilled and experienced operators, the installation of surgical tools is very time-consuming. How to improve the process efficiency is a huge challenge.
In the past, medical institutions used barcodes, laser marking, or QR codes to manage medical devices. However, it is quite difficult to read barcodes on surgical instruments. The use of laser marking is easy to cause rust and sticking dirt, and scanning the QR code to read the ID is time-consuming, RFID tags are a more practical option. They can be applied to various medical devices, not only adding numbers to the instruments but also writing and reading various information to record the use time and service life of the instruments. They facilitate efficient inventory checking and time use management and can be read in batches for rapid management, even if the instruments are stained with blood after surgery, thus making management easier.
In addition, through fast batch reading with RFID, operators can efficiently assemble and inspect toolsets, and the frequency of use of surgical instruments can be recorded as data and displayed on PC and other equipment. By measuring the use time of each tool, excessive inventory can be reduced and the use sequence can be recorded to optimize tool preparation before surgery.
The LXTBKZMCMG-010 UHF RFID tag produced by Murata is quite suitable for surgical instruments and medical instruments with metal surfaces. It is an innovative RFID module. The product can be used as an ultra-small tag, placed on any metal object, and used worldwide with high performance and high reliability.
The LXTBKZMCMG-010 UHF RFID tag is designed in a small package, using UHF band (865-928MHz), complying with ISO18000-63/EPC Global Gen2 (v2), with a size of 6.0 x 2.0 x 2.3 mm, using Impinj's Monza R6P, with a maximum reading range of 150cm (4WEIRP) on metal, complying with RoHS.
Murata produces RFID tags that can be used in metal applications. Besides, it can not be damaged in the process of autoclaving. When reading RFID tags, a hand-held reader-writer can be used to scan, or a fixed reader and antenna to read all surgical instruments on the table in real-time without manual operation. The reading range can reach 10cm-1m and may vary with the environment evaluated.
With RFID, small products can be traceable.
Many products need personalized settings (such as hearing aids), and product information needs to be recorded in each product, such as manufacturing records and amplifier settings, which need to be managed individually. However, due to the miniaturization of products, it becomes quite difficult to read information using conventional methods such as QR codes. Also, hearing aids are usually in direct contact with the skin, and the labels attached to the products may become dirty, which may hinder the smooth identification of the products. With RFID tags, centralized management can be carried out from the manufacturing stage to the after-sales market. Even if RFID tags are placed inside the product, they can be read from the outside, and the data can be rewritten repeatedly and have the characteristics of dirt resistance.
Murata's LXMSJZNCMF-198 and LXMS21NCNH-147 UHF RFID tags are innovative RFID modules that can be applied to monitoring products such as hearing aids, intelligent tracking equipment, medical kits and laboratory supplies (such as test tubes). This product can be used as an ultra-small label, attached to any metal object, non-metal object, and embedded into any object through glue, adhesive, double-sided adhesive tape, injection molding, etc., and has high performance and high reliability.
The LXMSJZNCMF-198 is designed in a compact, robust package that uses the UHF band (865-928MHz). The LXMSJZNCMF-198 complies with ISO18000-63/EPC Global Gen2v2 with a size of 1.2 x 1.2 x 0.55 mm and uses Impinj's Monza R6 with a reading range of 10mm, which complies with RoHS.
The LXMS21NCNH-147’s features are similar to those of the LXMSJZNCMF-198, except that the former complies with the ISO18000-63/EPC Global Gen2 (v1.2. 0) and is 2.0 x 1.25 x 0.55 mm in size using NXP's (NXP) G2iM.
Murata's RFID tags are small and robust and can be installed on a substrate and molded with resin. As such, the history of products can be tracked from the beginning of the manufacturing process. In addition, Murata can support antenna design, and RFID tags, and rely on RFID technical support to improve the efficiency of the manufacturing process and customer support.
RFID tag improves drug safety
Medication errors in medical institutions are also often heard. As to how to improve the safety of medications, RFID tags can be applied for drug control. Applying RFID tags to the certification of drug ampoules will prevent medication errors, and RFID tags can also be used to automatically record medication dosage, check whether the use time and validity period have expired or are wrong, which will help reduce the manpower required for medical site management.
The RFID tag can be installed inside the drug instead of on the outer package so that the drug can be prevented from being used incorrectly. Even if the drug is taken out of the package, it can be identified, and the coding equipment setting and prescription history records can be recorded in the RFID tag memory of each drug ampoule.
Murata’s RFID tag has a small and robust design and can be embedded into the product to maintain the current product design . RFID can store product information and usage history in rewritable memory (User memory, EPC memory). Password lock function prevents memory falsification. Each IC has unique, non-rewritable serial number, which can be used to verify product information. RFID tags can be installed by adhesive, double-sided adhesive tape, injection molding, etc. Non-contact reading can avoid the risk of wear and tear. Readers and tags can realize communication even if contaminated by chemicals and the like.

Conclusion
The NTC thermistors provided by Murata are applied to electronic thermometers. With RFID technology, they support medical safety applications. RFID tags can improve accuracy, eliminate human errors, verify products to protect brand value, and have lifelong tracking function, including providing RMA (Return Material Authorization) traceability, and increase the added value of products.
With the progress made in the medical field and the attention paid to health, the demand for medical applications is rapidly rising. Manufacturers interested in entering the medical market can quickly seize market opportunities with the help of Murata's solutions.
RELATED PRODUCT

