The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) defines three main classes for power supplies: Class I, Class II, and Class III. In this article from CUI Inc, understand the definitions for each of these classes and how to stay compliant.
These three classes are used to identify different methods for preventing the user of the power supply from being subjected to hazardous voltages from the input power source. Although it is easy to understand the differences in the IEC classes, many engineers are not familiar with the definitions and thus this article will present a quick explanation of the differences between the classes.
- 1. Class I - a layer of basic insulation and a grounded conductive chassis
- 2. Class II - double insulation (basic + supplemental) or reinforced insulation
- 3. Class III - no protection needed as the input voltage is not hazardous
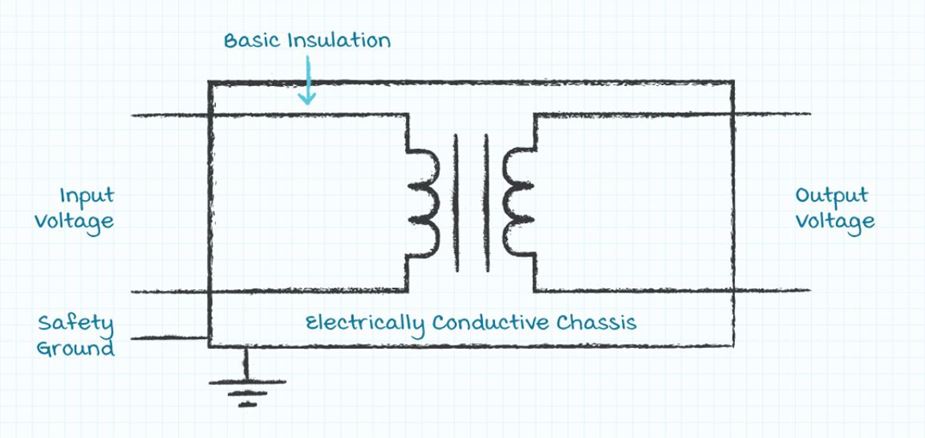
Class I Power Supplies
In IEC Class I power supplies the user is protected from hazardous input voltage levels by at least a layer of basic insulation and a grounded conductive chassis. The first level of safety protection is provided by basic insulation. The second level of safety protection is provided by the grounded conductive chassis. If there is a failure of the basic insulation, then any conductor with a hazardous voltage will be grounded by the conductive chassis before the hazardous voltage can come in contact with the user. All Class I power supplies must have safety ground brought to an electrically conductive chassis in the power supply.
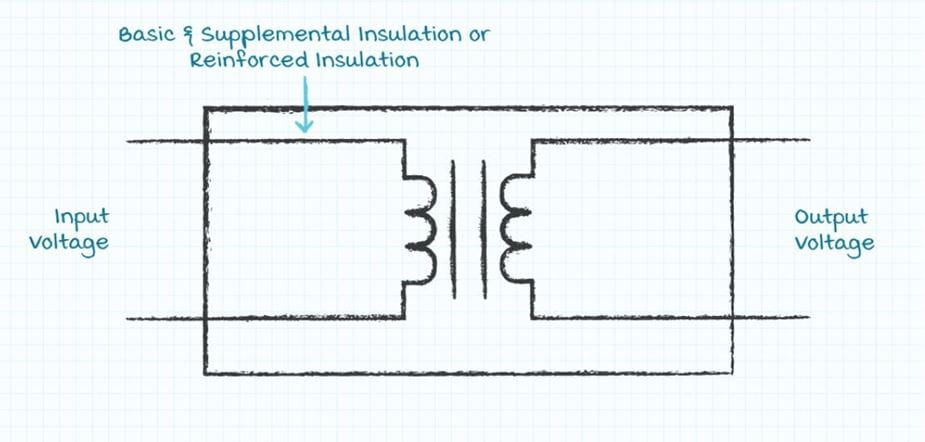
Class II Power Supplies
In IEC Class II power supplies the user is protected from hazardous input voltage levels by at least a layer of basic insulation and a layer of supplemental insulation or a layer of reinforced insulation. For double insulation, the first level of safety protection is provided by the basic insulation while the second level of safety protection is provided by the layer of supplemental insulation. Reinforced insulation provides the same safety factor as the combined basic and supplemental layers of insulation but in a single layer of insulation.
Because of double or reinforced insulation, IEC Class II power supplies are not required to have the safety ground conductor brought to the power supply.
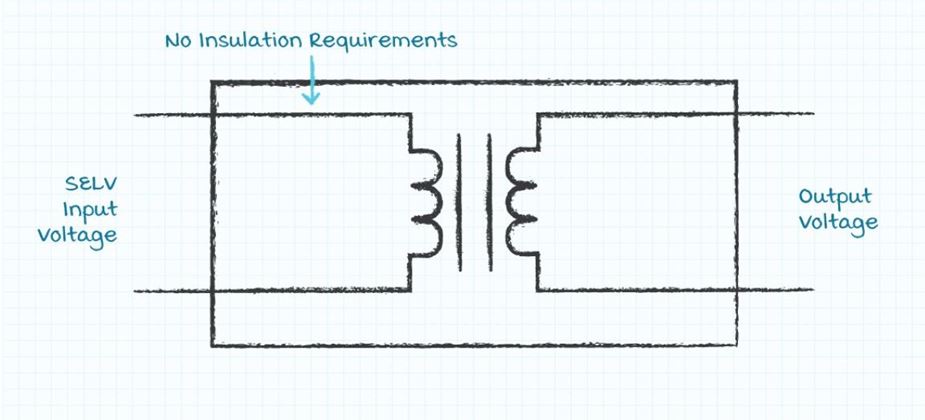
Class III Power Supplies
In IEC Class III power supplies the input voltage is not at a hazardous level and thus the user does not need to be protected from the input voltage. The IEC label for the non-hazardous input voltage is Safety Extra Low Voltage (SELV). The voltage in accessible parts of SELV circuits shall not exceed 42.4 Vac peak or 60 Vdc for longer than 200 ms., with an absolute limit of 71 Vac peak or 120 Vdc. SELV circuits must be separated from hazardous voltages by two levels of protection. The two layers of protection may be basic and supplemental insulation, reinforced insulation, or basic insulation combined with a safety grounded electrically conductive chassis.
Understanding the three IEC Power Supply Protection Classes enables those specifying or selecting power supplies to choose the appropriate class of supply based upon safety, regulatory, and cost constraints.

